I Always Disable These 3 Settings on My Router: Here's Why
SuperMSConfig - Optimisez votre Windows 11 comme un pro
Le 23 novembre 2024
par Korben -
Tutoriels-DiyOptimisation-SystemeAujourd’hui, les copains je vous propose d’explorer un petit outil bien sympa et surtout bien utile : SuperMSConfig. Ce dernier permet de transformer un bon vieux PC Windows 11 fraîchement installé en une machine de compétition, optimisée et personnalisée selon vos désirs les plus fous.
Vous connaissez sûrement déjà MSConfig, l’utilitaire intégré à Windows qui vous permet de gérer les paramètres de démarrage et certains pilotes système. C’est pratique pour désactiver des programmes au lancement ou modifier les options de démarrage du système. Cependant, ses capacités restent limitées et nécessitent souvent des manipulations un peu relous.
SuperMSConfig, comme son nom l’indique, va bien au-delà. Il repousse les limites en automatisant de nombreuses tâches que vous auriez dû effectuer manuellement dans MSConfig, et en offrant une chiée de fonctionnalités supplémentaires pour la gestion complète de votre système.
C’est qui qui a fuité aujourd’hui ?
We Can See All
We Can Delete All

Discover & control your digital footprint (DF) from a name, email, phone number and what it says about you!
Scan for stealer logs, breaches, credentials, and leaks with the OneSearch email scan below!
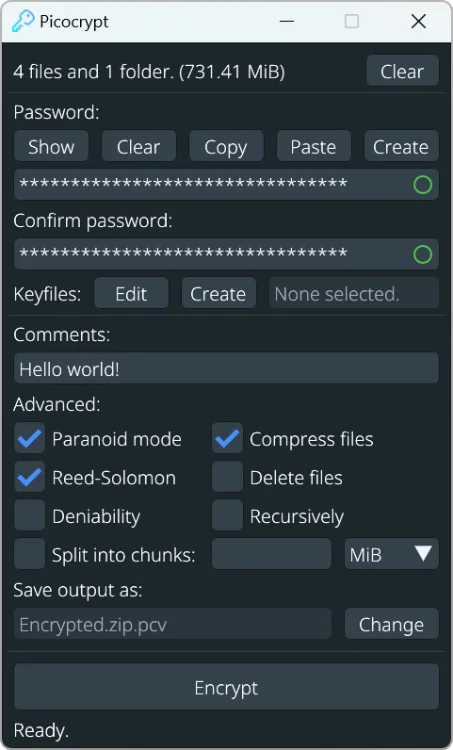
Picocrypt est un logiciel de cryptage simple, sécurisé et gratuit, utilisant le chiffrement XChaCha20 et la fonction de dérivation de clé Argon2id pour protéger vos fichiers. Il se distingue par sa légèreté, sa portabilité et son interface intuitive. Picocrypt offre des fonctions avancées telles que la protection contre la corruption de fichiers, l'utilisation de fichiers-clés…
Home Page
IP Address
JavaScript
WebRTC Leak Test
Canvas Fingerprint
WebGL Report
Font Fingerprinting
SSL Client Test
Geolocation API
Features Detection
Content Filters
Java Applet
Flash Player
Silverlight
More Tools
SettingsIt has long been believed that IP addresses and Cookies are the only reliable digital fingerprints used to track people online. But after a while, things got out of hand when modern web technologies allowed interested organizations to use new ways to identify and track users without their knowledge and with no way to avoid it.
BrowserLeaks is all about browsing privacy and web browser fingerprinting. Here you will find a gallery of web technologies security testing tools that will show you what kind of personal identity data can be leaked, and how to protect yourself from this.
Mise en place de la mise à jour automatique de liste de blocage DNS sous Windows 10
Website logo
Home
Frequently asked questions
Contact
My account
WFC screenshot
Windows Firewall Control - Managing Windows Firewall is now easier than ever
Program Overview
URLhaus
URLhaus is a project from abuse.ch with the goal of sharing malicious URLs that are being used for malware distribution.
EmoCheck
GitHub release Github All Releases
Emotet detection tool for Windows OS.
How to use
Download EmoCheck from the Releases page.
Run EmoCheck on the host.
Check the exported report.Distro_debian
Last edited by Steve Beattie 2 years ago
In Stock Debian
AppArmor should be available out of the box in the latest Debian distros. Please see http://wiki.debian.org/AppArmor
To enable the AppArmor in the Debian kernel, add “security=apparmor” to the kernel parameters, like this:
sed -i -e 's/GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX_DEFAULT="/&security=apparmor /' /etc/default/grub
This sed command results in the following /etc/default/grub line on my system:
GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX_DEFAULT=“security=apparmor quiet”
Then run
update-grub
Experimental AppArmor on Debian Jessie amd64
Kernel
Obtaining
mkdir -p ~/apparmor/ && cd ~/apparmor/
wget https://www.kernel.org/pub/linux/kernel/v3.x/linux-3.10.2.tar.xz
tar -xJf linux-3.10.2.tar.xz
cd linux-3.10.2/
Building
cd ~/apparmor/linux-3.10.2/
See if we can reuse the existing kernel configuration (CONFIG_IKCONFIG=y, CONFIG_IKCONFIG_PROC=y):
cp /proc/config.gz ./ && gzip -d config.gz
Tweak the kernel, enable AppArmor:
apt-get install libncurses-dev
make menuconfig
“Security options” ---> “AppArmor support”, “Enable AppArmor 2.4 compatability”
Installing
aptitude install dpkg-dev bc
cd ~/apparmor/linux-3.10.2/
make deb-pkg
dpkg -i ../linux-firmware-image_{version}.deb
dpkg -i ../linux-headers-{version}.deb
dpkg -i ../linux-image-{version}.deb
If the kernel is installed on another host, then symlinks for DKMS should be fixed.
rm /lib/modules/{version}/build; ln -s /usr/src/linux-headers-{version} /lib/modules/{version}/build
rm /lib/modules/{version}/source; ln -s /usr/src/linux-headers-{version} /lib/modules/{version}/source
About dpkg -i ../linux-libc-{version}.deb: /usr/include/x86_64-linux-gnu/asm seems to be missing from latest linux-libc-{version}.deb. If you installed linux-libc-{version}.deb, you can downgrade to Debian version with aptitude install linux-libc-dev=3.0.0-3.
Finally:
update-grub
Checking
Reboot under new kernel:
/sbin/shutdown -r now
or
reboot
Now see if AppArmor is loaded and enabled (should print “Y”):
cat /sys/module/apparmor/parameters/enabled
Tools
aptitude install apparmor apparmor-profiles
/etc/init.d/apparmor restart
Checking
cat /var/log/audit/audit.log | grep apparmor_parser
should display something like
type=AVC msg=audit(1316949034.097:108): apparmor=“STATUS” operation=“profile_load” name=“/bin/ping” pid=5207 comm=“apparmor_parser”
Tuning logs
Audit data by default is dropped into /var/log/messages via rsyslogd. That way, the data is severely capped by the kernel in order not to overload the messages log. To make audit data usable with AppArmor we should install auditd and tune it to keep large amounts of data:
apt-get install auditd
sed -i -re 's/max_log_file = [0-9]+/max_log_file = 200/' /etc/audit/auditd.conf
/etc/init.d/auditd restart
Sécuriser OpenSSH
21 Aug 2020
Sshd est le processus du serveur OpenSSH.
Il écoute les connexions entrantes à l’aide du protocole SSH et agit comme serveur pour le protocole.
Il gère l’authentification des utilisateurs, le chiffrement, les connexions de terminaux, les transferts de fichiers et le tunneling.
Home SSH Hardening Guides Contact
About
This free tool audits the configuration of an SSH server or client and highlights the areas needing improvement.
Too many admins overlook SSH configuration when setting up new systems. Unfortunately, the defaults for many operating systems are optimized for compatibility, not security.
To see a sample report, click here.
Multiple vulnerabilities found in Wireless IP Camera (P2P) WIFICAM cameras and vulnerabilities in custom http server
TL;DR: by analysing the security of a camera, I found a pre-auth RCE as root against 1250 camera models. Shodan lists 185 000 vulnerable cameras. The "Cloud" protocol establishes clear-text UDP tunnels (in order to bypass NAT and firewalls) between an attacker and cameras by using only the serial number of the targeted camera. Then, the attacker can automaticaly bruteforce the credentials of cameras.
Product Description
The Wireless IP Camera (P2P) WIFICAM is a Chinese web camera which allows to stream remotely.
shhgit finds secrets and sensitive files across GitHub (including Gists), GitLab and BitBucket committed in near real time.
secu ssh git password leaks
IP Leak Test DNS Leak Test What is my IP?